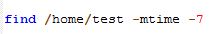
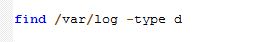
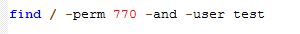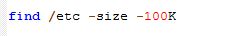Webmin is a free system administrator’s tool which gives the admin the direct configuration of the linux system through web. Thus eliminating the hard-to-remember linux commands. Actually this tool can be used for quick modifications on the linux system like setup user accounts, Apache, DNS, file sharing and much more. If you don’t know the exact commands to configure any aspects of the linux command line system, webmin is your tool.
Installation procedures:
- Download the webmin rpm through wget
- wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/webadmin/webmin-1.820-1.noarch.rpm
- installed required dependencies
- yum –y install perl perl-Net-SSLeay openssl perl-IO-Tty
- install web from the rpm package
- rpm –U webmin-*.rpm
That’ it. It now installed in your system. Now browser https://localhost:10000
If in case of SSL related problem and want to disable it, we can change it in configuration
vim /etc/webmin/miniserv.conf
and change the line containing
ssl=1
to
ssl=0
and open the link http://localhost:10000 again and login with your root account